肝素剂量反应曲线及肝素用量探讨
【摘要】 目的 非紫绀型先天性心脏病患儿群体化肝素剂量反应曲线及ACT(活化凝血时间)值达到480 s和750 s的最小肝素使用剂量。方法 将68例非紫绀型先天性心脏病患儿随机分为六组,进入手术室后常规进行生命体征监测及麻醉,监测并记录生理ACT值。体外循环开始前对六组患儿分别静脉注射肝素钠0.5 mg/kg、1 mg/kg、1.5 mg/kg、2 mg/kg、2.5 mg/kg、3 mg/kg,5min后采血监测并记录肝素后ACT值。记录每一位患儿的年龄、体重、身高、血常规、出凝血时间并计算体重指数。结果 非紫绀型先天性心脏病患儿群体化肝素剂量反应曲线为ACT=190.38×每公斤体重肝素剂量+114.71(r=0.8991)。使95%的患儿ACT值达到480 s的肝素使用剂量为(1.92±0.13)mg/kg,ACT值达到750 s的肝素使用剂量为(3.34±0.26)mg/kg。结论 非紫绀型先天性心脏病患儿ACT值达到480 s的肝素最小推荐使用剂量为2.05 mg/kg, ACT值达到750 s的肝素最小推荐使用剂量为3.60 mg/kg。
【关键词】 肝素 抗凝血 活化凝血时间 体外循环
Study of the Dose-Response Curve and Recommonded Dose of
Abstract: OBJECTIVE To draw the dose-reaction curve of heparin of congenital heart disease (CHD) patients and calculate the minimal heparin dose when actived clotting time (ACT) reached to 480 second and 750 second. METHODS Sixty-eight CHD patients were assigned randomly into six groups,monitoring and introduction as usual. Physiological ACT was monitored and recorded. Hepain was admitted to the six groups before cardiopulmonary bypass for the dose of 0.5mg/kg,1 mg/kg,1.5 mg/kg,2 mg/kg,2.5 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg, ACT was monitored after 300 seconds. The age, weight, height, RBC, Hgb, Hct, Plt, PT,APTT,TT and Fib of every patient were recorded. RESULTS The dose-response curve of heparin in CHD patients was ACT=190.38×(heparin dose per kg)+114.71(r=0.8991). The heparin dose when the ACT of 95% CHD patients reached to 480 seconds and 750 seconds were 1.92±0.13mg/kg and 3.34±0.26 mg/kg. CONCLUSION The minimal heparin dose of CHD patients when ACT reaches to 480 second and 750 second are 2.05 mg/kg and 3.60 mg/kg.
Key words: Heparin;Anticoagulation;Activated clotting time;Extracorporeal circulation
肝素抗凝是体外循环(extracorporeal circulation,ECC)心脏手术的必要环节,过与不及均影响患者术后的转归。目前按习惯方法使用肝素后相当一部分患者出现过度抗凝(ACT明显超出正常范围)。本文观察了先天性心脏病(CHD)患儿对不同剂量肝素的ACT反应,拟寻找CHD患儿ECC前肝素的适宜用量。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料 选择血常规、出凝血时间和肝肾功能正常,家族中无血液病史、术前未用过抗凝及抗血小板药物,体重大于10 kg的非紫绀型CHD患儿68例,随机分为六组,各组首次静脉注射肝素钠(天津生物化学制药厂生产,批号:051202,每毫克=125单位 )的剂量分别为0.5 mg/kg(n=14),1mg/kg(n=10),1.5 mg/kg(n=10),2 mg/kg(n=10),2.5 mg/kg(n=13)和3 mg/kg(n=11)。各组性别、年龄、体重、身高、体重指数、血常规、出凝血时间及生理ACT值均无统计学差异,见表1。
1.2 麻醉方法 所有病例均采用静吸复合全身麻醉,患者入手术室后静脉注射氯胺酮1~2 mg/kg,咪唑安定0.2 mg/kg,芬太尼0.01 mg/kg,哌库溴铵0.1 mg/kg,监测ECG,BP,SpO2,CVP, ETCO2等,术中予咪唑安定、芬太尼、哌库溴铵以维持适当的麻醉深度。
1.3 肝素给药与监测 麻醉诱导完成后,监测并记录患者的生理ACT值(美国ITC公司生产的ACT仪),等待术中切开心包后,从六种首次静脉注射肝素钠的剂量中随机选取其一行静脉注射,5min后经由非给药静脉通路采血测定并记录ACT值。ECC前补充肝素总量以达到2.5 mg/kg或3.0 mg/kg,再次测定ACT值。并记录性别、年龄、体重、身高、体重指数(bmi)、生理ACT值(ACT0) 、血常规(RBC,Hct,Hb,Plt)、出凝血时间(PT,APTT,TT,Fib)。
1.4 统计学处理 应用SPSS11.5软件进行统计学处理,用曲线拟合的方法绘制肝素剂量反应曲线,均数比较行F检验, P<0.05为存在统计学差异。
2 结 果
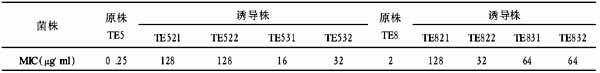
2.1 非紫绀型先天性心脏病患儿群体化肝素剂量反应曲线为ACT=190.38×肝素剂量(mg/kg)+114.71(r=0.8991)。使95%的患儿ACT值达到480 s的肝素使用剂量为(1.92±0.13)mg/kg,ACT值达到750 s的肝素使用剂量为(3.34±0.26)mg/kg。见图1。
2.2 非紫绀型先天性心脏病患儿ACT值达到480s的肝素最小使用剂量为2.05 mg/kg, ACT值达到750 s的肝素最小使用剂量为3.60 mg/kg。
3 讨 论
充分抗凝是保证ECC心脏手术患者安全的基本前提。ECC用于临床已50余年,在保证患者安全方面已取得明显进步,但如何监测和保证ECC中抗凝适当的问题尚未完全解决[1]。临床上使用的标准肝素是由猪肠粘膜或牛肺中提取、精制而成。分子量为5~30 kDa,平均为15 kDa,其中具有抗凝活性的肝素只占30%,故商品肝素均以抗凝活性效价单位标示。表1 患儿术前一般状况(肝素是体内、外均有效的抗凝剂,作用迅速。抗凝作用主要是通过血浆中的抗凝血酶Ⅲ (AT-Ⅲ)实现的[2-3],AT-Ⅲ是一种糖蛋白,分子量58kDa,是血浆中正常存在的抗凝物质,属于丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂家族。研究表明加强抗凝的管理及监测,合理掌握肝素用量能明显减少ECC术后的出血和输血量[4-6]。ECC中肝素常用量一般为300~400 u/kg[7-8]。
1975年Bull等[9]应用ACT监测ECC中肝素的抗凝效果,建立了肝素剂量-ACT曲线,使肝素用量个体化。报道[10-11],ECC前ACT和血浆肝素浓度有良好的相关性。传统的肝素剂量-ACT曲线为个体化曲线,通过肝素剂量-ACT曲线可以指导使ACT达到某一数值时的肝素用量,同时可以估计体内肝素量,在需要肝素拮抗时指导鱼精蛋白用量。由于ACT操作简单、准确,得到结果迅速、方便,室温下稳定等优点,使它几乎成为接近手术室内理想的抗凝监测方法,临床上广泛应用。ECC前必须肝素化,肝素化一般指ECC前硅藻土-ACT需达到480 s,如使用抑肽酶则ACT需大于750 s[5,12]。Young等[13]研究认为ECC安全的抗凝标准是ACT值至少要大于400 s。
然而,按传统剂量给药ACT值在大多数病例中往往明显大于480 s[14],甚至大于1000 s,造成过度抗凝。过度抗凝可引起血小板减少和功能障碍,肝素反跳,鱼精蛋白拮抗不完全,术后伤口引流量增加以及增加脏器出血的风险。通过此项研究,描绘了非紫绀型先天性心脏病患儿群体化肝素剂量反应曲线,并出使95%的患儿ACT值达到480 s的肝素使用剂量为(1.92±0.13)mg/kg,ACT值达到750秒的肝素使用剂量为(3.34±0.26)mg/kg。
通过进一步计算,得出非紫绀型先天性心脏病患儿ACT值达到480 s的肝素最小推荐使用剂量为2.05 mg/kg, ACT值达到750 s的肝素最小推荐使用剂量为3.60 mg/kg。远远低于以往肝素用量,既达到了充分抗凝的要求,又减小了出血量及肝素过量带来的不良反应[15]。
本文的研究对象为非紫绀型先天性心脏病患儿,手术中一般不使用抑肽酶,所以ACT值不需达到750 s,因此使95%的患儿ACT值达到480 s的肝素使用剂量2.05 mg/kg,对临床工作更有意义。从图1可以看出,在接近2.0 mg/kg的肝素剂量时,ACT值相对集中,离散度较小,所得结果更加准确。
【文献】
[1] Paul G,Bruce F,Robert K.临床麻醉学[M].王伟鹏主译.第四版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2004.803.
[2] Smythe MA. Advances in anticoagulation management: the role of pharmacy [J]. Ann Pharmacother,2007,41(3):493-495.
[3] Vats V,Nutescu EA, Theobald jc,et al. Survey of hospitals for guidelines, policies, and protocols for anticoagulants [J]. Am J Health Syst Pharm,2007,64(11):1203-1208.
[4] 纪宏文,邓硕曾. 体外循环心脏手术后异常出血的原因分析[J]. 循环杂志,1998,1:59-60.
[5] Shuhaibar MN,Hargrove M,Millat MN,et al. How much heparin do we really need to go on pump? A rethink of current practices [J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2004,26(5):947-950.
[6] Jobes DR, Aitken GL, Shaffer GW. Increased accuracy and precision of heparin and protamine dosing reduces blood loss and transfusion in patients undergoing primary cardiac operations [J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,1995,110:36-45.
[7] Bull BS,Korpman RA,Huse WM,et al. Heparin therapy during extracorporeal circulation.Ⅰ Porblems inherent in existing heparin protocols [J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,1975,69: 674-684.
[8] Paul G ,Bruce F,Robert K .Clinical Anesthesia[M].第四版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2004.804.
[9] Bull BS, Huse WM, Brauer FS,et al. Heparin therapy during extracorporeal circulation.Ⅱ The use of a dose-response curve to individualize heparin and protamine dosage [J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,1975,69: 685-689.
[10] Giavarina D,Carta M,Fabbri A,et al. Monitoring high-dose heparin levels by ACT and HMT during extracorporeal circulation: diagnostic accuracy of three compact monitors [J]. Perfusion,2002,17(1):23-26.
[11] Tremey B,Szekely B,Schlumberger S,et al. Anticoagulation monitoring during vascular surgery: accuracy of the Hemochron low range activated clotting time (ACT-LR)[J]. Br J Anaesth,2006,97(4):453-459.
[12] Guzzetta NA,Miller BE, Todd K,et al. An evaluation of the effects of a standard heparin dose on thrombin inhibition during cardiopulmonary bypass in neonates[J]. Anesth Analg,2005,100(5):1276-1282.
[13] Young JA, Kisker CT, Doty DB. Adequate anticoagulation during cardiopulmonary bypass determined by activated clotting time and the appearance of fibrin monomer[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,1978,26(3):231-240.
[14] Owings JT, Pollock ME, Gosselin RC,et al. Anticoagulation of children undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass is overestimated by current monitoring techniques[J]. Arch Surg, 2000,135(9):1042-1047.
[15] Ovrun E. Completely heparinized cardiopulmonary bypass and reduced systemic heparin: clinical and hemostatic effects[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,1995,60(2):365-371.