辛伐他汀对高脂血症患者颈动脉内膜中层厚度及凝血系统的影响
【关键词】 颈动脉
Effect of simvastatin on intimamedia thickness of common carotid artery and coagulative system in hyperlipidemic patients
【Abstract】 AIM: To observe the nonlipidlowering effect of simvastatin on the intimamedia thickness(IMT)and coagulative system in hyperlipidemic patients. METHODS: Fortysix hyperlipidemic patients were given simvastatin 20 mg, qd for 12 weeks and the changes of TC, TG, LDLC, HDLC, IMT, fibrinogen (FIB), thrombin time (TT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and prothrombin time (PT) were observed. RESULTS: TC, TG, LDLC, FIB decreased significantly (P<0.001) in hyperlipidemic patients after 12 weeks and IMT also decreased significantly (P<0.001). HDLC and PT increased significantly (P<0.001) and so did TT and APTT(P<0.001). CONCLUSION: Simvastatin has both lipidlowering and nonlipidlowering effect, which decreases the IMT of the common carotid arteries and improves the coagulative system.
【Keywords】 simvastatin; carotid artery; IMT; blood coagulative
【摘要】 目的:观察辛伐他汀对高脂血症患者颈动脉内膜中层厚度(IMT)及凝血系统的变化及其非调脂作用. 方法:高脂血症患者46例口服辛伐他汀20 mg,Qd, 12 wk,分别于前后观察IMT、血脂总胆固醇(TC)、三酰甘油(TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDLC)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDLC)、纤维蛋白原(FIB)、凝血酶原时间(TT)、活化部分凝血酶时间(APTT)、凝血酶原时间(PT)改变. 结果:血脂紊乱组治疗12 wk后的颈动脉IMT变薄(P<0.001);TC, TG, LDLC, FIB均有显著降低(P<0.001),HDLC升高(P<0.001),TT, APTT 均有显著延长(P<0.001). PT升高(P<0.001). 结论:调脂作用的辛伐他汀有效调脂同时可发挥其非调脂作用,干预、延迟颈动脉IMT的进程,改善凝血系统,减低血液黏稠度.
【关键词】 辛伐他汀;颈动脉;内膜中层厚度;血液凝固
0引言
他汀类药物可以有效降低血脂总胆固醇(TC),三酰甘油(TG),低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDLC),在一定程度上升高高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDLC). 近期研究又发现,他汀类药物治疗的临床益处远远超出其调脂产生的调控血脂作用,其非调脂机制已渐引起临床的重视,尤其对动脉血管内皮功能障碍、平滑肌增生、迁移的抑制及凝血机制的影响在临床上的作用备受关注[1]. 本研究旨在通过对颈动脉内膜中层厚度(IMT)及凝血机制的观察,评价他汀类药物的非调脂作用.
1材料和方法
1.1材料
高脂血症患者为血脂紊乱组46(男26,女20)例,年龄34~83(平均60.6±10.4)岁,血清TC≥5.70 mmol/L,或合并TG≥1.77 mmol/L,LDLC≥3.00 mmol/L,HDLC≤1.00 mmol/L. 同时排除糖尿病、高血压病、甲状腺疾病及肝肾疾病.
1.2方法
血脂紊乱组每日服用辛伐他汀(Simvastatin,商品名舒降之,杭州默沙东制药有限公司生产)20 mg,1次/d,共12 wk. 治疗前和12 wk后采用日本Model全自动生化分析仪测TC,TG,LDLC,HDLC;ACL200血凝仪测纤维蛋白原(FIB),凝血时间(TT),活化部分凝血酶时间(APTT),凝血酶原时间(PT);采用HP5500心脏B超测量颈动脉IMT. 所有研究对象在试验期间不使用其他影响血脂代谢和凝血机制的药物.
统计学处理:SPSS 10.0统计分析,组内数据进行方差齐性检验,治疗前后计量资料以x±s表示并采用twosample ttest. IMT与凝血各指标及血脂结果进行相关分析. P<0.05认为有统计学意义.
2结果
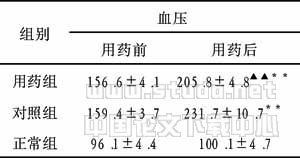
血脂紊乱组治疗12 wk后与治疗前比较,TC,TG, LDLC 均显著降低(P<0.001),HDLC明显升高(P<0.001, Tab 1). 血脂紊乱组辛伐他汀治疗12 wk后颈动脉IMT (0.73±0.05) mm与治疗前(0.91±0.03) mm比较, P<0.001,IMT变薄. 血脂紊乱组治疗12 wk后与治疗前比较,TT,APTT,FIB显著降低(P<0.001).PT均有改善(P<0.001,Tab 2).表1血脂紊乱组辛伐他汀治疗12 wk前后血脂变化(略)表2血脂紊乱组辛伐他汀治疗12 wk前后凝血指标变化(略)
血脂紊乱组亚组分析,单纯高脂血症与混合型高脂血症患者IMT,FIB,TT,APTT和PT之间比较差异无统计学意义. 颈动脉IMT变化与凝血指标PT,TT,APTT,TG,LDLC和HDLC无相关关系; IMT变化与血脂结果TC,TG,LDLC和HDLC无相关关系.
血脂紊乱组1例服药后1 wk出现轻度恶心、乏力及腹胀,1例服药即出现轻度口周麻木,继续服用后症状均自行消失,未退出试验.
3讨论
高脂血症患者的血脂异常(高LDLC,高TG,高TC,低HDLC及相应比例的失衡)是重要的致动脉硬化(AS)因素,可以引起动脉内皮细胞功能障碍,内膜下脂质沉着及中层平滑肌的增殖与迁移,加速颈动脉IMT的进程. 他汀类药物可以竟争性地抑制胆固醇生物合成初始阶段的限速酶3羟基3甲基戊二酰辅酶A(HMGCoA),从而减少胆固醇的生物合成,加强血液中LDL及LDL前体的清除[2]. 通过增加细胞凋亡减少兔子和人的主动脉平滑肌细胞的数量,延迟AS的进程. 减少FIB,巨噬细胞和平滑肌细胞总数[3-5]. Knapp等[6]还发现他汀类药物可以通过刺激某些蛋白质构型的变化,使得其调控诱导血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的敏感性增加,抑制血管平滑肌细胞增殖及迁移. Undas等[7] 发现20 mg/d辛伐他汀3 m后可减少凝血酶原、Va因子、XIII因子的生成,降低血清FIB含量. 随机双盲对照试验提示辛伐他汀(simvastatin)、普伐他汀(pravastatin)可明显降低凝血反应[8]. 另有研究提示辛伐他汀通过上调Ⅲ型内皮eNOS的作用,进而减少血小板的聚集[9,10]. 本结果表明,在高脂血症患者应用辛伐他汀治疗后可显著降低LDLC,TG及TC,轻度HDLC增加,改善血凝机制,降低血液黏稠度,使颈动脉IMT明显变薄. 逆转或延迟颈动脉IMT的作用不单一依赖于调脂作用或调脂外的改善凝血机制作用,而是两者的协同作用[11].
【】
[1] Brown BG, Zhao XQ. Importace ofendothelial function in mediating thebenefits of lipidlowering therapy[J]. Am J Cardiol, 1998;82:49T-52T.
[2] Corti R, Fayad ZA, Fuster V, et al. Effects of lipidlowering by simvastatin on human atherosclerotic lesions[J]. Circulation, 2001;104:249-252.
[3] Fukumoto Y, Libby P, Guasch JF, et al. Statins alter smooth muscle ceel accumulation and collagen content in established atheroma of watanabe heritable hyperlipidmic rabbits[J]. Circulation, 2001;103:993-999.
[4] Rauch U, Osende JI, Chesebro JH, et al. Statin and Cardiovasculer disease: the multiple effects of lipidlowering therapy by statins[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2000;153:181-189.
[5] Gotto FM. Lipidlowering therapy for the primary prevention of coronary heart disease[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1999;33:2078-2082.
[6] Knapp AC, Huang J, Starling G, et al. Inhibitors of HMGCOA reductase sensitize human smooth muscle cells to Fasligand and cytokineinduced cell death [J]. Atherosclerosis, 2000;152:217-227.
[7] Undas A, Brummel KE, Musial J, et al. Simvastatin depresses blood clotting by inhibiting activation of prothrombin, factor V, and factor X III and by enhancing factor Va inactivation[J]. Circulation, 2001;103:2248-2253.
[8] Joukhadar C, Klein N, Prinz M, et al. Related Articles. Similar effects of simvastatin, simvastatin and pravastatin on thrombogenic and inflammatory parameters in patients with hypercholesterolemia[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2001;85:47-51.
[9] Laufs U, Geryz K, Huang P, et al. Simvastatin upregulates type III nitric oxide synthase in thrombocytes, decreases platelet activation, and protects from cerebral ischemia in normocholesterolemic mice[J]. Stroke, 2000;31:2442-2449.
[10] 苗懿德,孙宁玲,周惠清,等. 辛伐他汀降脂治疗对老年人血管内皮功能及颈动脉内膜中膜厚度的影响[J]. 动脉硬化杂志,2001;9(5):420-423.
Miao YD, Sun NL, Zhou HQ, et al. Effect of simvastatin on endothelial function and intimamedia thickness of carotid arteries in elderly patients[J]. Chin J Arterioslerosis, 2001;9(5):420-423.
[11] 林培林,王涛,李雅男,等. 阿托伐他汀对高脂血症患者颈动脉内膜中层厚度及凝血系统的影响[J]. 高血压病杂志, 2004;12(1):21-23.