感染性疾病中血清降钙素原和C反应蛋白检测的临床意义
作者:高阜宏,乔世岩,黎明新
【关键词】 ,降钙素原;C反应蛋白;感染
[摘要] 目的:探讨感染性疾病中血清降钙素原(PCT)和C反应蛋白(CRP)的变化及其临床意义。方法:检测100例感染性疾病和40例非感染性疾病血清中PCT、CRP的含量。结果:细菌感染组与病毒感染组、非感染组比较PCT、CRP明显升高,差异有显著性(P<0.01)。病毒感染组与非感染组比较PCT、CRP轻度升高,差异无显著性(P>0.05)。细菌感染组前后PCT、CRP比较差异有显著性(P<0.01)。结论:感染时,PCT、CRP的检测有助于疾病的鉴别诊断,动态检测其变化对疗效判断有一定的价值。
[关键词] 降钙素原;C反应蛋白;感染
Determination of Serum Procalcitonin and Creactive Protein in Infection Diseases
Abstract:Objective To study the serum procalcitonin (PCT) and Creactive protein (CRP) in infection diseases and its clinical significance.Methods The contents of PCT and CRP insera of 100 and 40 noninfected cases of newborn were examed.Results The levels of PCT and CRP in bacteria infected group were significantly higher than that in virus infected and noninfected groups(P<0.01).The levels of PCT and CRP in virus infected group were slightly hightly higher than that in noninfected group and there was no significicant difference among them(P>0.05).In the bacteria infected group there were significant differences between the pretreament levels of PCT and CRP and post treatment levels of them(P<0.01).Conclusion The examination of serum PCT and CRP is helpful to make distinctive diagnosis for infections at earlystage,and the dynamic determination of their level change is valuable for judgement of therapeutic results.
Key words:Procalcitonin;Creactiveprotein;Infection
全身性感染是危重症患者的主要死亡原因之一,单其临床表现常缺乏特异性[1,2],且感染病原体的检查需要一定的时间周期,往往影响对感染的诊断和治疗,造成不良后果。因而准确地诊断感染并采取有效治疗措施对于危重症患者具有十分重要的意义。降钙素原(Procalction,PCT)是降钙素的前体,含有116个氨基酸,正常情况下由甲状腺C细胞产生。越来越多的资料表明[3~6]:PCT是细菌或真菌感染早期的一个诊断指标,感染时血清PCT水平升高,并与感染的严重程度和预后密切相关[7]。C反应蛋白(CRP)是肝脏细胞在IL6的作用下分泌产生的一种急性时相蛋白,在应急情况下血清CRP水平增高。本文旨在探讨血清PCT和CRP水平在诊断危重症患者的感染性与非感染性状态中的作用。
1 对象和方法
1.1 对象 2003年1月至2003年12月住院患者140例,平均年龄(57.4±20.6)岁。其中男80例,女60例。感染组:肺炎、感染性休克、败血症、腹泻等100例以血清学检测和病原体分离、培养作为细菌或病毒感染的依据,其中细菌感染组60例,男34例,女26例;病毒感染组40例,男25例,女15例;非感染组40例,男21例,女19例。
1.2 方法 抽取3 ml静脉血,凝固后离心分离血清,置-20 ℃冰箱中备查。PCT的测定,采用德国BRAHMS公司免疫发光法定量检测试剂盒测定,按说明书操作;CRP的水平采用免疫比浊法在KONEPRO生化分析仪用RANDOX试剂进行定量测定,按说明书操作,正常值为0 mg/L~6 mg/L。
1.3 统计学方法 定量资料采用t检验,呈正态分布的分类资料采用χ2检验,以P<0.05差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
细菌感染组与病毒感染组和非感染组患者血清PCT、CRP检测结果相比较,差异有显著性(P<0.01)。结果见表1。
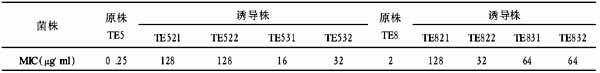
表1 治疗前细菌感染组与病毒感染组和对照组PCT、CRP检测结果(略)
注:a与b、c比较,P<0.01;b与c比较,P>0.05。细菌感染组治疗前PCT为(23.1±7.9) μg/L,CRP为(26.7±17.7) mg/L;治疗后分别为(2.1±0.7) μg/L,(4.9±0.9) mg/L,治疗前后相比差异有显著性P<0.01。
3 讨论
PCT是一种无激素活性的糖蛋白,血清PCT的半衰期为25 h~30 h[8],通过免疫荧光法可进行PCT的检测。该种检测方法示正常健康人PCT的血浆水平小于0.1 μg/L,而严重细菌感染患者血中PCT水平升高,PCT可能是细菌感染的特异性指标[9]。本文结果显示,在细菌感染时,血清PCT水平明显升高,而在病毒感染组血清PCT水平却无明显升高,因此,血清PCT的检测可在感染性疾病中用以鉴别细菌感染还是病毒感染;动态观察其变化,还可作为判断抗生素疗效和预后的一项指标,还可作为选用抗生素的一项依据[10],从而避免滥用抗生素,减少细菌耐药的产生。CRP是评价感染所致炎症反应的一种有效工具,本组结果显示,细菌感染后CRP明显升高,病情缓解,CRP逐渐下降至正常;而病毒感染组却无明显升高。因此,CRP对临床疗效的监测有一定的价值。国外研究报道[11],对感染性患者同时测定血CRP和PCT,发现PCT的升高早于CRP的上升。在局部感染时,PCT一般不升高,而CRP会升高,在没有全身表现的感染时,CRP可能是一个重要的观察指标,在有全身表现的严重感染时,PCT可能是一个较好指标[12]。因此,同时监测、动态观察PCT和CRP,并结合临床,更有助于观察疾病的演变和抗生素疗效。
参考:
[1] Carlet J.Rapid diagnosis methods in detection of sepsis[J].Infect Dis Clin North Am,1999,128:483494.
[2] Neda S,Nishio K,Minamino N,et al.Increased plasma level of adrenomechillin in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,1999,60:3236.
[3] BalcI C,Sungurtekin H,Gurses E,et al.Usefulness of procalcitonin for diagnosis of sepsis in the intensive care unit[J].Crit Care,2003,7:8590.
[4] American College of Chest physicians/society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference.Definitions for sepsis and multiple organ failure and guideline for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis[J].Crit Care Med,1992,152:529535.
[5] Assicot M,Cendrel D,Carsin H,et al.High serum procalcitonin concentrations in patients with sepsis and infection[J].Lancet,1993,341:515518.
[6] AINawas B,Shah PM.Procalcitonin in patents with and without immunosuppression and sepsis[J].Infection,1996,24:434436.
[7] Werra I,Jaccardin S,et al.Cytokines,nitrite/nitrate,soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors and procalcitonin concentration:comparrions in patients with sepsis shock cardiogenic shock and bacterial pneumonia[J].Crit Care Med,1997,25:607613.
[8] Karzai W,Oberhoffer M,Meier Hellmann A,et al.Procalcitonina new indicator of the systemic response to severe infections[J].Infection,1997,25:329334.
[9] Assicot M,Gendrel D,Carsin H,et al.Highserum Procalcitonin concentrations irpatients with sepsis and infection[J].Lamcet,1993,341:515518.
[10] Lorrot M,Moulin F,Coste J,et al.Procalcitonin in pediatric emergencies;comparison with Creactve protein,interleukin 6 and interferom alpha in the differentiation between bacterial and viral infections[J].Presse Med,2000,29(3):128134.
[11] Monneret G,Labaune JM,Isaac C,et al.Procalcitonin and Creactive protein levels in neonatal infections[J].Actapaediatr,1997,86:209212.
[12] 单海燕,张伟利,储凇雯.测定全身严重感染的一个新指标降钙素原[J].上海医学,2001,24(11):699701.