面神经下颌缘支的应用解剖
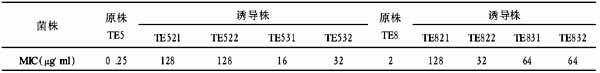
【摘要】 目的 了解面神经下颌缘支的正常层次解剖位置,为涉及面侧区和颌下区的美容外科手术提供临床应用解剖学资料。方法 解剖33具(共66例)成人尸体标本的头颈部标本,观察了面神经下颌缘支的分支类型、走行、与面动脉的位置关系以及穿出腮腺处和与面动脉的交叉处的体表位置。结果 面神经下颌缘支为1~2支,以单干型居多,约占58%,大多行于下颌骨下缘上方约占44%,行于骨下缘下方者占5%。未发现面神经下颌缘支不与面动脉交叉,位置在均下颌角下缘上、下方约0.5~1 cm范围内。面神经下颌缘支经过面动脉的浅面和深面者分别占89%和6%;面神经下颌缘支穿出腮腺处的体表位置分别在下颌角上方和下颌支后缘前方1 cm交点附近,面神经下颌缘支与面动脉交处距下颌支后缘约4 cm,距下颌骨下缘约1 cm。结论 面神经下颌缘支的毗邻和行程关系较为复杂,了解其与周围结构的重要位置关系,可以减少美容外科手术因神经损伤造成下唇及口角功能障碍的发生。
【关键词】 面神经下颌缘支;应用解剖学;美容外科
[Applied anatomy of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve
Abstract: Objective To address the anatomical position of anatomic location of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve,providing clinical anatomical data for cosmetic surgery on the side and submaxillary region. Methods Totally 33 cases (66 sides) autopsies were observed, including the types and courses of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerves and their surface locations and relations with the facial artery in the area of heads and necks. Results A single trunk marginal mandibular branches accounts for 58%, the branches witch run along the upper and lower inferior border of border of mandible account for 44% and 5%.The surface location of the branches running out of the parotid gland is near the intersection between 0.5 to 1.0 cm above mandibular angle and the anterior of the posterior border of the mandible.The marginal mandibular branches which pass superficially and deep to the facial artery account for 89% and 6%, respectively. The surface location of the branches running out of the parotid gland is near the intersection between 1.0 cm above mandibular angle and the anterior of the posterior border of the mandible. The distances from the intersection between the nerve and the facial artery to the posterior border of the marginal mandibular branch and to lower border of the mandible were 4.0 cm and 1.0 cm, respectively. Conclusion Marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve has a complicated adjacent and course, so understanding the adjacent relationships can reduce the nerve injury during cosmetic surgery.
Keywords: marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve; applied anatomy; aesthetic surgery
面神经下颌缘支的走行有许多变异,在颌下部施行某些美容外科手术时,往往易受损伤而导致口角及下唇运动障碍。目前有关面神经下颌缘支的应用解剖学资料不多[1],尤其是体表定位资料尚少,面神经下颌缘支的应用解剖对颌下部美容外科手术有实际指导意义。为此作者对面神经下颌缘支的分支类型、走行、面神经下颌缘支与面动脉的位置关系以及面神经下颌缘支穿出腮腺处与面动脉交叉处进行了体表定位测量,以期为美容外科手术提供临床应用解剖学资料。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
选取经福尔马林浸泡的头颈部保存完好的成人尸体标本33具(男19具,女14具)共66例。
1.2 解剖方法
采取逐层剖析,翻开皮瓣后,修净皮下组织,游离颈阔肌至口角高度以上,剖开腮腺鞘,在腮腺组织中仔细分离辨认面神经腮腺丛,在腮腺前下端寻找面神经下颌缘支的起点,仔细追踪直至末稍部。重点观察下颌缘支的行程、分型、与面动脉的位置关系[2]。用精确度为0.01 mm的游标卡尺测量面神经下颌缘支穿出腮腺处和与面动脉交叉处至下颌支后缘的水平距离和至下颌骨下缘的垂直距离。
1.3 统计学处理
用t检验进行统计学处理,所有数据用(±s)表示。
2 结果
2.1 面神经下颌缘支的走行
面神经下颌缘支为1~2支,多数为1支,均发自下颌角与耳垂的连线中点处,多数在腮腺下缘浅出(约67%),少数在前缘和前下缘的转折处出腮腺(约29%),发出后稍呈孤形,自咀嚼肌附着点处后缘至颏肌深面,沿下颌体下缘之上、下前行。在下颌角前方约3.5 cm处越过面动脉的浅、深面,然后进入颈阔肌和下颌体之间前行并分支入肌[3]。
2.2 出腮腺处及与面动脉交叉处距下颌支后缘和下颌骨下缘的距离
面神经下颌缘支穿出腮腺的体表位置大多在下颌角上方1 cm与下颌支后缘前方1 cm的交点附近;面神经下颌缘支与面动脉交叉的位置距下颌支后缘约4 cm,距下颌骨下缘约1 cm。
2.3 面神经下颌缘支的支数与分型
面神经下颌缘支从腮腺前下缘穿出后可分为3种类型:①合干型,先为单干,然后分成2支,在进入降口角肌和降下唇肌深面前方又合成单干,以上、下干发出若干细支,此型占(16.93±1.23)%;②单干型,在起止中,本干为1支,由本干发出分支较少,此型占(57.72±2.64)%;③双干型,本干有2支,相互平行,多数下干比上干稍粗,由上、下干各发出分支,此型占(25.61±2.17)%。
2.4 面神经下颌缘支与下颌骨下缘的位置关系
面神经下颌缘支自腮腺浅出后的行径可分为三种情况:①行于下颌骨下缘上方,沿下颌体咬肌筋膜内行走,距下颌骨下缘(0.61±0.21) cm,占(43.83±2.86)%;②大致平下颌骨下缘,相当于下颌骨下缘与下颌下腺之间的沟内行走,达咬肌前缘处,弯向前上与面动脉交叉后,分支进入降口角肌,降下唇肌和颏肌,距下颌骨下缘(0.17±0.11) cm,占(51.24±3.91)%;③行于下颌骨下缘下方,距下颌骨下缘(0.63±0.14) cm,最低不超过0.5 cm,占(5.21±0.87)%。
2.5 面神经下颌缘支与面动脉的位置关系
面神经下颌缘支本干与面动脉的位置未发现面神经下颌缘支本干不与面动脉交叉者。面神经下颌缘支与面动脉形成交叉关系有三种类型:①面神经下颌缘支位于面动脉浅面者占(88.94±6.71)%;②面神经下颌缘支位于面动脉深面者占(6.39±1.15)%;③面神经下颌缘支分两支经其浅面或深面夹持或环抱面动脉,然后合成1支,占(7.83±0.96)%。
3 讨论
面神经下颌缘支为1~2支,多数为1支,均发自下颌角与耳垂的连线中点处,多数在腮腺下缘浅出占67%,少数在前缘和前下缘的转折处出腮腺,占29%[4],面神经下颌缘支穿出腮腺的体表位置,大多(87%)在下颌角上方1 cm与下颌支后缘前方1 cm的交点附近;面神经下颌缘支与面动脉交叉的位置距下颌支后缘约4 cm,距下颌骨下缘约1 cm。面神经下颌缘支单干型居多,约占58%,大多行于下颌骨下缘上方约约0.5 cm处(44%),行于骨下缘下方者占5%;未发现面神经下颌缘支不与面动脉交叉者,而且在下颌骨下缘上、下方0.5~1 cm的位置较为恒定。因此,沿下颌骨下缘2 cm以下作手术切口,可避免伤及此神经[5]。在颌下区作手术时,切口不宜过深,在颈阔肌与颈深筋膜浅层之间剥离,可避免损伤面神经下颌缘支。如果损伤单干型或合干型的本干,则可导致运动障碍,故手术中应注意保护面神经下颌缘支。面神经下颌缘支分支间有较丰富吻合,其形态和特征各异,损伤面神经下颌缘支能引起同侧下唇和口角下垂的畸形。此外,下颌缘支的肌支与肌支间有丰富吻合,提示口唇肌肉的运动可通过支的吻合获得神经传导通路的代偿;又因下颌缘支本干有时为二支,因此,只伤及其中一支,引起面部畸形可能不明显[6?9]。
总之,只有掌握了面神经下颌支及其分支的分布、走行及与面部组织的正常层次解剖关系,在面侧区及颌下区的美容外科手术才能达到满意的效果。
【】
[1] 李云峰,李静平,何 军.面部除皱术的应用解剖研究[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2007,28(3):294-295.
[2] Ramirez OM. The subperiosteal approach for the correction of the deep nasolabial fold and the central third of the face[J]. Clin Plast Surg, 1995, 22(2):341-356.
[3] Stuzin JM, Baker TJ, Gordon HL, et al. Extended SMAS dissection as an approach to midface rejuvenation[J]. Clin Plast Surg, 1995, 22(2):295-311.
[4] de la Fuente A, Santamaria AB. Endoscopic subcutaneous and SMAS facelift without preauricular scars[J]. Aesth Plast Surg, 1999,23(2):119-124.
[5] Nagase T, Yoshimura K, Aiba E, et al. Angle?splitting ostectomy followed by face lift for elderly patients with prominent mandibular angles [J]. Plast Reconstruct Surg, 2005, 115(2) :633-640.
[6] 刘安堂,江 华.面神经颊支和下颌缘支的解剖及临床应用研究进展[J].临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(1):106-108.
[7] Hwang K, Cho HJ, Battuvshin D, et al. Interrelated buccal fat pad with facial buccal branches and parotid duct[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2005,16(4):658-660.
[8] Toure S, Vacher C, Bertrand JC. Anatomy of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve[J]. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac, 2004,105(3):149-152.
[9] Potgieter W, Meiring JH, Boon JM, et al. Mandibular landmarks as an aid in minimizing injury to the marginal mandibular branch:A metric and geometric anatomical study[J]. Clin Anat, 2005,18(3):171-178.