[javascript]图解+注释版 Ext.extend()
Ext.extend() 体现了程序员非凡的制造轮子的能力。它基于 javascript 古老的对象模型,最大程度地模拟出现代面向对象语言的类型继承的语意。但是在程序界有太多的“与XXX很像”,但是实际上又有很多差别。要想最彻底、最精确地理解 Ext.extend(),最直接(往往也是最有效)的方法就是去读它的源代码。为了达到更好的可读性,我更改了部分变量名称,加上了详细的注释。
1 /**
2 * <p>Extends one class to create a subclass and optionally overrides members with the passed literal. This method
3 * also adds the function "override()" to the subclass that can be used to override members of the class.</p>
4 * For example, to create a subclass of Ext GridPanel:
5 * <pre><code>
6 MyGridPanel = Ext.extend(Ext.grid.GridPanel, {
7 constructor: function(config) {
8
9 // Create configuration for this Grid.
10 var store = new Ext.data.Store({...});
11 var colModel = new Ext.grid.ColumnModel({...});
12
13 // Create a new config object containing our computed properties
14 // *plus* whatever was in the config parameter.
15 config = Ext.apply({
16 store: store,
17 colModel: colModel
18 }, config);
19
20 MyGridPanel.superclass.constructor.call(this, config);
21
22 // Your postprocessing here
23 },
24
25 yourMethod: function() {
26 // etc.
27 }
28 });
29 </code></pre>
30 *
31 * <p>This function also supports a 3-argument call in which the subclass's constructor is
32 * passed as an argument. In this form, the parameters are as follows:</p>
33 * <div class="mdetail-params"><ul>
34 * <li><code>subclass</code> : Function <div class="sub-desc">The subclass constructor.</div></li>
35 * <li><code>superclass</code> : Function <div class="sub-desc">The constructor of class being extended</div></li>
36 * <li><code>overrides</code> : Object <div class="sub-desc">A literal with members which are copied into the subclass's
37 * prototype, and are therefore shared among all instances of the new class.</div></li>
38 * </ul></div>
39 *
40 * @param {Function} superclass The constructor of class being extended.
41 * @param {Object} overrides <p>A literal with members which are copied into the subclass's
42 * prototype, and are therefore shared between all instances of the new class.</p>
43 * <p>This may contain a special member named <tt><b>constructor</b></tt>. This is used
44 * to define the constructor of the new class, and is returned. If this property is
45 * <i>not</i> specified, a constructor is generated and returned which just calls the
46 * superclass's constructor passing on its parameters.</p>
47 * <p><b>It is essential that you call the superclass constructor in any provided constructor. See example code.</b></p>
48 * @return {Function} The subclass constructor from the <code>overrides</code> parameter, or a generated one if not provided.
49 */
50 Ext.extend = function(){
51 // inline overrides
52 var io = function(o){
53 for(var m in o){
54 this[m] = o[m];
55 }
56 };
57 var oc = Object.prototype.constructor; // 如果一个对象的 constructor == oc,说明它是使用类似 { age:22 } 这种语法创建的字面量对象,
58 // 而且没有对constructor属性赋值
59
60 return function(subClass, superClass, overrides){
61 if(typeof superClass == 'object'){
62 // 如果 superClass 是对象而不是构造函数,就说明是使用的是
63 // var Cat = Ext.extend(Animal, {
64 // say : function() {
65 // document.writeln("I'm a cat name " + this.name);
66 // }
67 // });
68 // 这种方式调用的。也就是说返回值是subClass, subClass 参数其实是 superClass,superClass参数其实是overrides,overrides参数应该被忽略 www.2cto.com
69 overrides = superClass; // 忽略 overrides 参数
70 superClass = subClass; // subClass 参数其实是 superClass
71 // subClass 参数将作为将来的返回值。
72 // 如果 overrides 对象没有自定义构造函数,为其定义一个,并且里面调用父类构造函数;
73 // 如果 overrides 对象含有自定义构造函数,把overrides的构造函数赋给子类
74 subClass = overrides.constructor != oc ? overrides.constructor : function(){
75 superClass.apply(this, arguments); // 调用父类构造函数(前提是子类构造函数的参数可以比父类少,但是顺序要一致)
76 };
77 }
78
79 // 原型式继承。之所以创建一个临时构造函数F,而不是令 subClass.prototype = new SuperClass,
80 // 是为了更改子类的prototype的时候不会影响到父类的prototype
81 var F = function(){},
82 subPrototype, // 子类构造函数的 Prototype
83 superPrototype = superClass.prototype; // 父类构造函数的 Prototype
84
85 F.prototype = superPrototype;
86 subPrototype = subClass.prototype = new F();
87 subPrototype.constructor=subClass;
88 // 只所以没写成 subClass.superclass=superClass,是为了在overrides对象的constructor方法里
89 // 可以使用诸如 “MyGridPanel.superclass.constructor.call(this, config)”这种(读起来比较
90 // 自然的)写法调用父类构造函数。
91 subClass.superclass=superPrototype;
92 // 如果 superclass.prototype 是字面量对象,确保 superclass.prototype。constructor 指向 superClass
93 if(superPrototype.constructor == oc){
94 superPrototype.constructor=superClass;
95 }
96 // 为子类增加一个override()方法。调用 subClass.override(o) 等价于调用 Ext.override(subClass, o)
97 subClass.override = function(o){
98 Ext.override(subClass, o);
99 };
100 // 增加一个名为 superclass() 的实例方法,这样在overrides对象的constructor方法里
101 // 就可以使用诸如 “this.superclass().constructor.call(this, config)”来调用父类
102 // 构造函数,而且没有依赖子类构造函数的名称。
103 subPrototype.superclass = subPrototype.supr = (function(){
104 return superPrototype;
105 });
106 // 为子类增加一个实例方法: override()
107 subPrototype.override = io;
108 // 将 overrides 对象里的方法复写到 subClass.prototype 中
109 Ext.override(subClass, overrides);
110 // 为子类增加一个extend()方法。调用 subClass.extend(o); 等价于调用 Ext.extend(subClass, o);
111 subClass.extend = function(o){return Ext.extend(subClass, o);};
112 return subClass;
113 };
114 }();
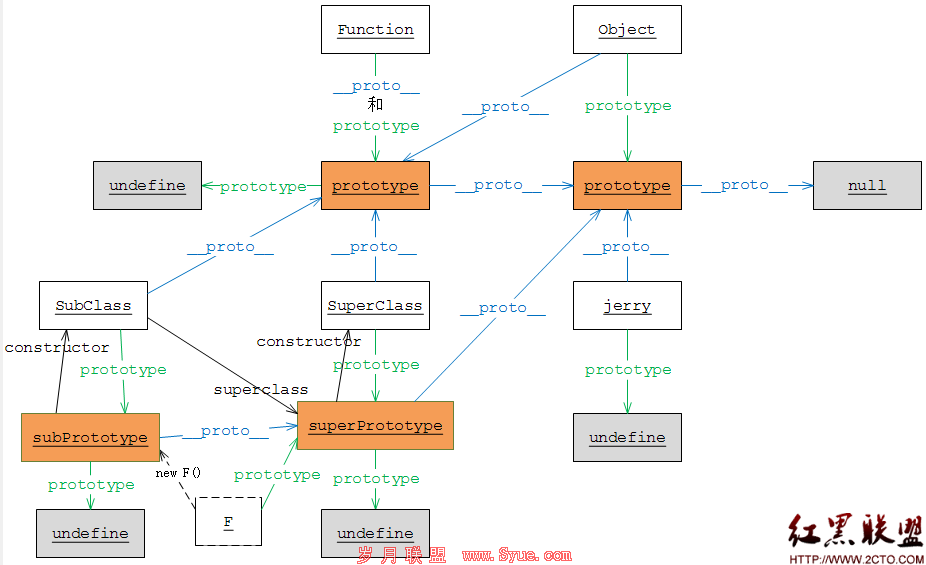
下面这张对象图则是执行了 var SubClass = Ext.extend(SuperClass, { someprop : 'some' }) 之后的效果。
作者 景春雷