Python基础(1)
来源:岁月联盟
时间:2012-10-08
--print....
print 'Hello World' #(2.x)
print ('Hello World') #(3.x)
--stdout
import sys
sys.stdout.write('Hello World!/n')
2、general rules
--use '#' to start a comment
--one statement per line,unless semicolon used more than one statement per line
--code blocks delimited by indentation
--use '/' to break up long lines
3、simple statements fit on one line,no code block following
4、compound statements have code block
--fist line called a header
--indented sub-block of code called a suite
--header plus ':' followed by indented suite
--indentation allows any whiltespace
==use spaces not tabs
==use same # of spaces for each line
5、Variables
--dynamic typing....variables not declared
==type inferred on assignment
==var = expression
--flexible assignment syntax
==var1 = var2 = xepression
==var1, var2 = exp1, exp2 #it equals to var1=exp1;var2=exp2
6、Assignment
--primary assignment operator:=
--augmented assignment:+=,*=,.....
--++,-- are not permitted
7、identifier rules (similar to other language)
--fist character must be alphabetic
--any others can be alphanumeric
--treat underscores (_) as alphabetic
--case-sensitive
8、Python gotchas
--special names begin/end with underscores
==avoid using until you know what...
**they are used for
**you are doing
--do not use built-in function/data names
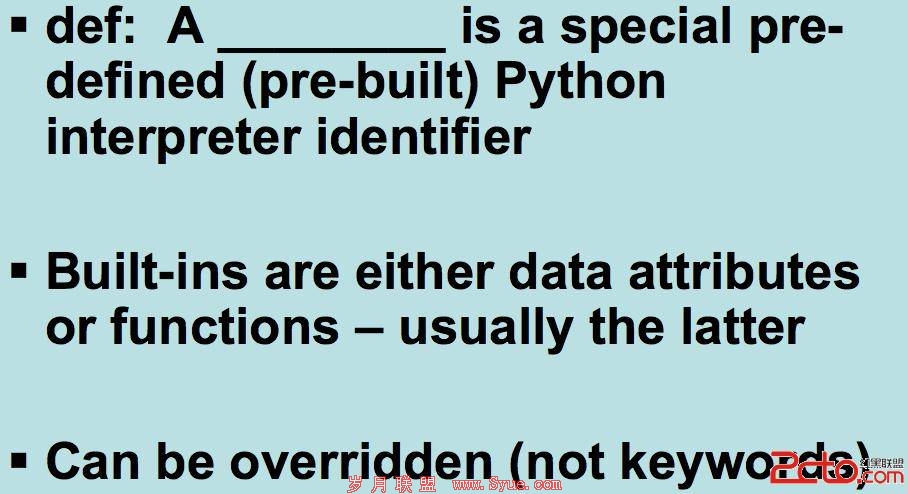

--reserved words,or keywords,can't be used

9、Function
--declared using def keyword

--declarations:
==header line and at least one for body
==can have any number of arguments
--if no value explicitly returned...
==Python returns None
**None: Python's NULL or void
**None: constant Boolean False
10、Importing & Modules
--Allows use of outside code
--What are Modules
==Self-contained Python code
==Bring in new functionality/objects
==Import only features that you need
--two different ways to access module attributes
== Use module elements with name (I preferred)
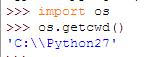
== Can import individual elements into "namespace"

11、Keyboard input
-- get keyboard input from user
== use Python's raw_input() function
== renamed to input() in Python 3.x
-- Syntax:
-- Example:

上一篇:python中的数据模型
下一篇:零基础写py爬虫