用VB2005构建反应灵敏的应用程序
来源:岁月联盟
时间:2007-02-01
Visual Basic .NET中最突出的特色之一就是构造多线程应用程序。但由于多线程应用程序天然的复杂性及挑战性,使许多VB开发人员没有充分利用这一新提供的功能。
在了解Visual Basic 2005创建多线程应用程序是多么容易以前,让我们看一看通常程序开发人员所遇到的挑战:长时间运行的任务在执行过程中经常限制了用户的输入或使用户无法与操作系统进行交互。
一、长时间运行的任务实例
在这个实例中,我们将对一个规定的整数计算斐波纳契数列(每个数等与数列前两个数之和)。也许这个例子对开发人员开发应用程序来说用处不大,但它的确是一个非常合适的例子,它不需要开发人员具备数据库或是其他一些必须得知识。你想象的应用程序中的长时间运行的任务类型可能是耗时的数据库操作、遗传系统调用、外部服务调用或是其他的一些深层次的资源操作。
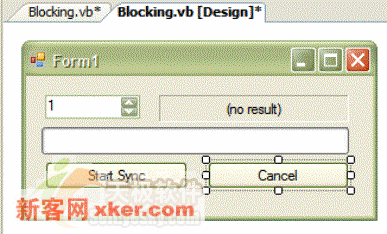
为了创建这个项目,首先创建一个窗体应用程序,它带有一个进度条、两个按钮、一个数字输入框和一个显示结果的标签。两个按钮分别命名为startSyncButton 和cancelSyncButton,将标签的text属性设置为no result。对窗体上的各个控件进行仔细布局调整以后,界面效果如下:
在这个窗体中添加以下代码计算斐波纳契数列。
Function ComputeFibonacci(ByVal n As Integer) As Long
’ The parameter n must be >= 0 and <= 91.
’ Fib(n), with n > 91, overflows a long.
If n < 0 OrElse n > 91 Then
Throw New ArgumentException( "value must be >= 0 and <= 91", "n")
End If
Dim result As Long = 0
If n < 2 Then
result = 1
Else
result = ComputeFibonacci(n - 1) + ComputeFibonacci(n - 2)
End If
’ Report progress as a percentage of the total task.
Dim percentComplete As Integer = CSng(n) / CSng(numberToCompute) * 100
If percentComplete > highestPercentageReached Then
highestPercentageReached = percentComplete
Me.ProgressBar1.Value = percentComplete
End If
Return result
End Function
这段代码非常直观,它通过递归调用来计算结果。尽管在小数情况下这段代码将执行的非常快,但随着你输入的数字的增大,代码的执行时间迅速增加。
每执行代码时,这个函数将更新一次屏幕上的进度条,以提醒用户当前程序进度及应用程序正在运行。

Private Sub startSyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles startSyncButton.Click
’ Reset the text in the result label.
result.Text = [String].Empty
’ Disable the UpDown control until
’ the synchronous operation is done.
Me.numericUpDown1.Enabled = False
’ Disable the Start button until
’ the synchronous operation is done.
Me.startSyncButton.Enabled = False
’ Enable the Cancel button while
’ the synchronous operation runs.
Me.cancelSyncButton.Enabled = True
’ Get the value from the UpDown control and store it
’ in the globle variable numberToCompute.
numberToCompute = CInt(numericUpDown1.Value)
’ Reset the variable for percentage tracking.
highestPercentageReached = 0
’ Start the synchronous operation.
result.Text = ComputeFibonacci(numberToCompute).ToString
’ Enable the UpDown control.
Me.numericUpDown1.Enabled = True
’ Enable the Start button.
startSyncButton.Enabled = True
’ Disable the Cancel button.
cancelSyncButton.Enabled = False
End Sub
正如其他应用程序一样,这里没有什么特别之处,当用户点击开始按钮后,程序开始计算并将结果现在是屏幕上,但是,这个程序有一个非常明显的错误。
当按下按钮后,主线程既要对来自于用户界面的操做进行反应,又要忙于计算斐波纳契数列值。如果你开始这个应用程序并输入一个大的数字,例如50,你将看到你的应用程序将给用户带来的窘境。点击Start按钮后,试着将应用程序最小化或移动程序窗口,这时应用程序将没有任何反应或反应非常迟钝。
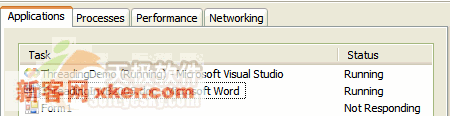
除了反应迟钝或根本没有任何反应外,没有别的方法来让用户取消进程。如果用户错误地输入了一个大的数字并且其不愿意继续等待,那么他该怎么做呢?
为了说明这一点,在Cancel按钮后添加如下代码:
Private Sub cancelSyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object,_
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles cancelSyncButton.Click
MsgBox("Cancel")
End Sub
这段非常简单的代码将显示一个消息框,表明我们已申请了取消操作,如果你在程序运行时输入另外一个较大的数字,那么当你点击取消按纽时程序将没有任何反应,尽管程序在运转。
最好的解决上述问题的办法是将需要长时间运行的任务放入另外一个线程之内,这将让我们的主线程接受用户操作并让应用程序及时做出相应的反应。

二、使用后台工作者的多线程例子
在Visual Basic 6.0中要解决多线程的问题如果不使用定时器的话几乎是不可能的事。在Visual Basic .NET中,就显得比较容易,只要创建一个thread对象,并给它传递一个你希望运行的方法,然后调用thread对象的开始方法就可以了。代码如下:
Dim myThread As New Thread(AddressOf MyFunction)
myThread.Start()
然而,强大的功能也意味着要承担巨大的责任。尽管Visual Basic .NET可以简单地创建并使用一个线程,但在开发程序时不得不小心谨慎,以免出现问题或BUG。
由于正确设计程序非常复杂,因此对于广大Visual Basic爱好者来说多线程并没有广泛地使用。然而,随着Visual Basic 2005的推出,由于使用了后台工作者组件,这个过程变的更容易而且更安全了。
为了说明创建多线程应用程序是多么容易,并且程序对用户的反应是多么灵敏,让我们创建一个名叫MultiThreaded的新窗体,窗体布局和代码同上,然而这次两个按钮分别命名为startAsyncButton、 cancelAsyncButton,因为这次我们将异步执行我们的代码,并且不阻塞主线程的运行。
对于我们的新窗体要做的第一件事是以设计模式打开它,并从工具箱的"组件"部分拖放一个后台工作者组件到窗口上。你还要在属性窗口中将该组件的WorkerReportProgress 、WorkerSupportsCancellation属性设置为"TRUE"。正如你将看到的,这些属性设置将允许我们更新进度条、终止进程。
Private Sub startAsyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles startAsyncButton.Click
’ Reset the text in the result label.
result.Text = [String].Empty
’ Disable the UpDown control until
’ the asynchronous operation is done.
Me.numericUpDown1.Enabled = False
’ Disable the Start button until
’ the asynchronous operation is done.
Me.startAsyncButton.Enabled = False
’ Enable the Cancel button while
’ the asynchronous operation runs.
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = True
’ Get the value from the UpDown control.
numberToCompute = CInt(numericUpDown1.Value)
’ Reset the variable for percentage tracking.
highestPercentageReached = 0
’ Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync(numberToCompute)
End Sub
你可能注意到我们将调用后台工作者组件的RunWorkerAsync方法,并在这之后省去了所有的代码。
当你想在一个独立的线程执行代码时,你可以调用RunWorkerAsync方法。这将在后台工作组件对象中产生DoWork事件。在这个事件中我们将计算斐波纳契数列值。
’ This event handler is where the actual work is done.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_DoWork( _
ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DoWorkEventArgs) Handles backgroundWorker1.DoWork
’ Get the BackgroundWorker object that raised this event.
Dim worker As System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker= CType(sender, System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker)
’ Assign the result of the computation
’ to the Result property of the DoWorkEventArgs
’ object. This is will be available to the
’ RunWorkerCompleted eventhandler.
e.Result = ComputeFibonacci(e.Argument, worker, e)
End Sub
我们可以直接将代码放在这里来处理异步过程,但是在大多数情况下还是将其放在一个独立的程序中更好。在我们的例子中将使用现存的ComputeFibonacci,仅仅是作了一些小的改动而已。
Function ComputeFibonacci( ByVal n As Integer, _
ByVal worker As System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker, _
ByVal e As System.ComponentModel.DoWorkEventArgs) As Long
’ The parameter n must be >= 0 and <= 91.
’ Fib(n), with n > 91, overflows a long.
If n < 0 OrElse n > 91 Then
Throw New ArgumentException( "value must be >= 0 and <= 91", "n")
End If
Dim result As Long = 0
’ Abort the operation if the user has canceled.
’ Note that a call to CancelAsync may have set
’ CancellationPending to true just after the
’ last invocation of this method exits, so this
’ code will not have the opportunity to set the
’ DoWorkEventArgs.Cancel flag to true. This means
’ that RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs.Cancelled will
’ not be set to true in your RunWorkerCompleted
’ event handler. This is a race condition.
If worker.CancellationPending Then
e.Cancel = True
Else
If n < 2 Then
result = 1
Else
result = ComputeFibonacci(n - 1, worker, e) + ComputeFibonacci(n - 2, worker, e)
End If
’ Report progress as a percentage of the total task.
Dim percentComplete As Integer = CSng(n) / CSng(numberToCompute) * 100
If percentComplete > highestPercentageReached Then
highestPercentageReached = percentComplete
worker.ReportProgress(percentComplete)
End If
End If
Return result
End Function
开发人员在使用Visual Basic开发多线程程序时最常见的错误是试图操作另外线程创建的成员对象,例如用户界面线程。这将产生不可预期的、千奇百怪的错误,因为并不是每一个对象对于线程都是安全的。
第一件你将注意的事是我们将向后台工作者以及事件参数传递计算函数。这将允许我们在后台激活事件,主线程负责更新控件,如进程条等。
每次调用ComputeFibonacci时,我们将调用后台工作者组件的ReportProgress方法,每当我们这么作时组件的ProgressChanged事件将得到触发。这个事件将返回到主线程来更新进度条。为了避免线程交叉,我们没有在新的线程中更新进度条。
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged( _
ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As ProgressChangedEventArgs) _
Handles backgroundWorker1.ProgressChanged
Me.progressBar1.Value = e.ProgressPercentage
End Sub
这时如果编译运行程序,你将发现即使你输入一个大的数字,也可以最大最小化应用程序,或是立即移动应用窗口。这是因为主线程用来响应用户操作而第二个线程用来进行计算。
因为主线程用来响应用户的操作,因此,我们可以在Cancel按钮后输入如下代码,来给用户提供退出应用程序的能力。
Private Sub cancelAsyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)Handles cancelAsyncButton.Click
’ Cancel the asynchronous operation.
Me.backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync()
’ Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = False
End Sub
注意到为了退出后台处理线程,我们只是简单地调用了后台工作者的CancelAsync方法,这个函数将组件的CancellationPending属性设置为TRUE,每次调用计算函数时都将对这个属性进行检查。
当计算函数完成了任务,后台工作者组件将抛出RunWorkerCompleted事件,在这个事件中我们的代码将显示计算结果、重置屏幕上的按钮,并为下次操作做准备。
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted( _
ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As _
RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs) _
Handles backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerCompleted
’ First, handle the case where an exception was thrown.
If Not (e.Error Is Nothing) Then
MessageBox.Show(e.Error.Message)
ElseIf e.Cancelled Then
’ Next, handle the case where the user canceled the
’ operation.
result.Text = "Canceled"
Else
’ Finally, handle the case where the operation succeeded.
result.Text = e.Result.ToString()
End If
’ Enable the UpDown control.
Me.numericUpDown1.Enabled = True
’ Enable the Start button.
startAsyncButton.Enabled = True
’ Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = False
End Sub
三、结论
我希望上述的例子代码已经向你显示了在Visual Basic 2005中使用后台工作组件的属性、方法和事件进行多线程编程是多么的容易。只要微小的一些修改,我们就可以创建一个交互式的应用程序,为了向用户提供最优秀并且高度互动的应用程序,你应该使用多线程,它将长时间运行的任务从用户界面线程中解脱出来。

下一篇:探索VB系列中的事件处理的奥秘