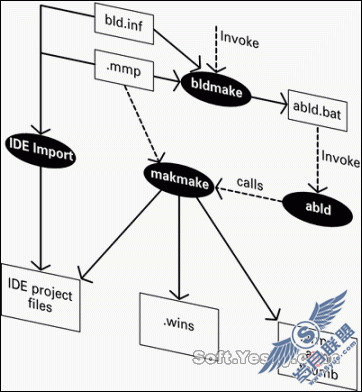
HDU OJ 2586 How far away ?[LCA的Tarjan离线算法]
来源:岁月联盟
时间:2012-08-05
思路:若用 一般的 最短路 来写,时间复杂度比较高,会超时。这题时利用 LCA的Tarjan离线算法
LCA 就是 求 点 i,j 的最近公共祖先 k: d [ ] 代表根节点(可任取一点做根节点)到任意一点的距离,d [ i ] + d [ j ] - 2*d [ k ] 、就是 i ,j 间的距离。
LCA的实现: DFS+并查集 (假设求 i j 的最近公共祖先)即为
在 DFS搜到 一个点(比如 i)时,判断 是否 要求 该点与其他点(比如 j)的LCA。
(1)若有,判断 j 点是否 已经搜到过了?,若搜到过 并查集中 j 的 根(父)节点即为 i 和 j 的最近 公共祖 先!! 若 j 之前未 搜到,继续向下搜索别的点(比如k),然后令 father[ k ]=i ;
(2)没有,继续向下搜别的点(比如k),然后令 father[ k ]=i ;
具体一些细节,参考代码;
AC代码:
[cpp]
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int d[410000],loop[410000],n,m;
int father[410000],AC[400000];
const int inf=0x7fffffff;
struct sb /*询问*/
{
int x;
int a;
};
struct hello /*存地图*/
{
int x;
int d;
};
struct node /*队列优先级*/
{
friend bool operator<(node t1,node t2)
{
return t1.d>t2.d;
}
int x;
int d;
};
vector<hello> V[41000];
vector<sb>F[41000];
void dis()
{
int a,b,i,j;
d[1]=0;
priority_queue<node> P;
node t1={1,0};
P.push(t1);
while(!P.empty())
{
i=P.top().x;
P.pop();
if(loop[i])
continue;
loop[i]=1;
for(a=0;a<V[i].size();a++)
{
int k=V[i][a].x;
if(loop[k]==0&&d[k]>d[i]+V[i][a].d)
{
d[k]=d[i]+V[i][a].d;
node t2={k,d[k]};
P.push(t2);
}
}
}
}
int find(int k)
{
if(k!=father[k])
return father[k]=find(father[k]);
return father[k];
}
void init()
{
int a,b;
for(a=1;a<=n;a++)
{
father[a]=a;
d[a]=inf;
loop[a]=0;
}
}
void dfs_lca(int k)
{
loop[k]=1;
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<F[k].size();i++)
{
if(loop[F[k][i].x])
{
int tt=find(F[k][i].x);
//printf("-------%d %d %d/n",k,F[k][i].x,tt);
AC[F[k][i].a]=d[k]+d[F[k][i].x]-2*d[tt];
}
}
for(i=0;i<V[k].size();i++)
{
if(loop[V[k][i].x]==0)
{
dfs_lca(V[k][i].x);
father[V[k][i].x]=k;
}
}
}
void output()
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
printf("%d/n",AC[i]);
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
V[i].clear();
F[i].clear();
}
}
int main()
{
int a,b,c,ncase;
int x,y,z;
scanf("%d",&ncase);
for(c=1;c<=ncase;c++)
{
if(c>1)
printf("/n");
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
init();
for(a=1;a<n;a++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z);
hello t1={y,z};
V[x].push_back(t1);
hello t2={x,z};
V[y].push_back(t2);
}
for(a=1;a<=m;a++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(x==y)
{
AC[a]=0;
continue;
}
sb t1={y,a};
F[x].push_back(t1);
sb t2={x,a};
F[y].push_back(t2);
}
dis();
memset(loop,0,sizeof(loop));
dfs_lca(1);
output();
}
}
/*
12 12
1 2 3
1 3 3
2 4 3
2 5 3
2 6 3
3 7 3
3 8 3
4 9 3
5 10 3
5 11 3
7 12 3
4 1
4 2
4 3
4 4
5 6
9 8
11 2
8 2
7 8
9 3
10 11
5 10
*/
作者:PIAOYI0208